Frameworks in Project Management

Project management is an ever-changing field that requires a number of methods to be successful. Learning well-known project management techniques can help you become an industry expert.
The project management system is a set of principles, strategies, and procedures used by those working in the field. Not only do advanced systems differ in the way they are designed, but they also require different delivery, workflow, and project management software development.
How to manage a project:
The project management method provides a clear project guide with all the steps needed to successfully deliver a project. These project strategies or strategies provide a defined management framework, process guidelines, evaluation tasks, processes, and submissions. They take a detailed, robust, and repetitive approach to project management.
Framework project management:
The project management framework provides structure and direction for the project. However, unlike project management methods it is less detailed and less robust. Frameworks direct projects to their goals while being flexible enough to adapt to changing circumstances.
Framework vs. Methodology:
Framework:
- Describes how guidelines can be implemented.
- Creates space for creative adaptation.
- Experts’ preferred choice.
- Creating and implementing performance metrics is difficult.
- Allows for the inclusion of other practices and tools.
Methodology:
- Provides rigid rules and practices for completing a project.
- It’s pretty prescriptive and rigid.
- Beginner-friendly.
- Describes all performance guidelines in detail.
- Cannot be integrated with other practices and tools.
Methodologies for managing projects: 10 popular frameworks: 1. Agile
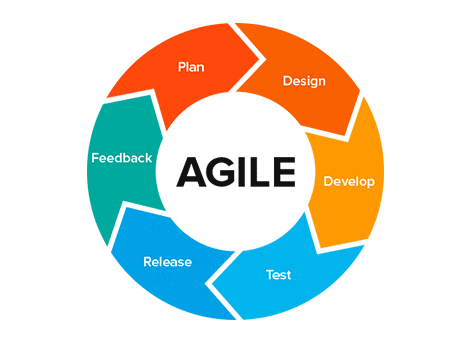
What it is: The Agile approach is the most frequently used methodology. But instead, it could be better defined as a principle of project management.
The basis of an Agile approach is:
1. It’s data-backed and Iterative in nature.
2. The individuals are valued over processes.
3. Collaborativeness
4. Speed and effectiveness.
Teams prefer to opt for specific methodologies while using Agile when it comes to implementing Agile in place. It includes various other methodologies like Scrum, Kanban, extreme programming, crystal, or even Scrumban. Since a more detailed approach produces a well-rounded project management philosophy and a tangible plan for delivering great work by connecting Agile methodology with it.
Who should use it: Due to universal principles Agile could be used by any team. The decision of which methodology to use with it is the real task.
2. Waterfall
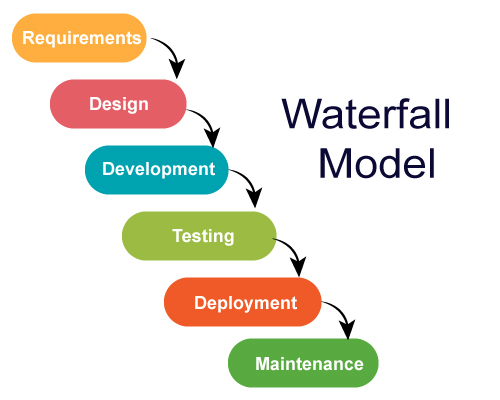
What it is: The waterfall model is considered to be a traditional framework, that is pretty straightforward. Also popularly known as software development life cycle (SDLC), this linear process cascades down, which is sorted and is in a sequential fashion.
Waterfall methodology approach:
As every task depends on the previous task, its completion before the next task is crucial. It ensures that work stays on track and helps to have clear communication throughout the process.
Who should use it: Being detailed, it could be used in large projects when it consists of different and multiple stakeholders. A better choice for the creation of a predictable and thoroughly planned-out project plan. also thanks to the clear steps throughout the project and dependencies that contribute to tracking workflow to achieve goals.
3. Scrum

What it is: The Scrum methodology project cycle includes the usage of short sprints. Unlike Waterfall, it consists of a team organization of 10 or less with a cycle span of a week or two.
One of its unique features includes the usage of a Scrum master, project manager leading daily Scrum meetings, sprints, demos after each sprint is completed. Meets ensure timely completion of tasks and help to connect project stakeholders.
Scrum is often associated with an Agile framework. Due to its similar principles, like valuing individuals over processes and collaboration.
Who should use it: Scrum methodology should be used by Agile user teams as well for it provides flexibility. As sprints here are split into small teams, Teams using the Agile approach should try it once as it can work for both large and small teams.
4. Kanban

What it is: The Kanban methodology includes representation of project backlogs using boards as visual elements. Used by Agile teams for better visualization workflows and is crucial to reduce bottleneck conditions in a project progress. Also, it uses a software tool to drag and modify boards within projects.
Many teams use it their own way due to its undefined process method. If you aim to keep the framework simple and focus on the most important project tasks, Kanban is the best choice.
Who should use it: Due to its visual board methods, any team who needs to stay on track irrespective of the geography should Prefer Kanban over others. Hence remote-first teams are most benefited from it.
5. Scrumban

Scumban is an inspirational approach to both Scrum and Kanban. Some think that it is an integrated approach that combines the best of each.
How to manage a Scumban project:
which uses a sprint cycle similar to Scrum but allows each function to be dragged into the system like Kanban. This allows for the most important work to be completed and keeps the project plans simple. Scumban also uses Scrum meetings to help improve collaboration and keep goals high in mind.
Who can Use Scumban: If you like the idea of splitting a project into smaller tasks, but similarly and want to keep it simple in appearance, Scumban is very useful for you. It takes into account both simplicity and clarity.
6. PRINCE2
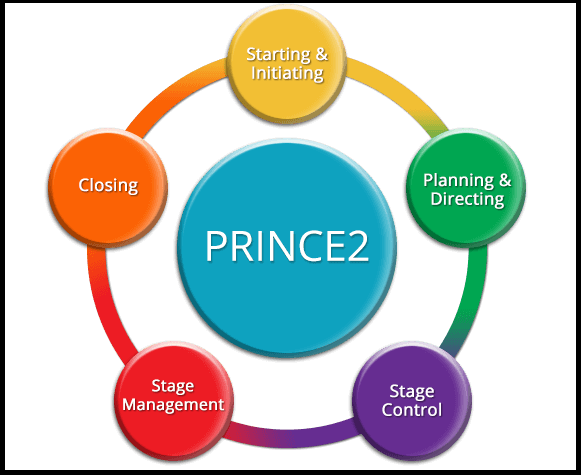
PRINCE2, also known as Projects IN Controlled Environments that uses the most advanced drainage method to define the different phases within a project. It was originally created by the UK government for IT projects and is still aligned with larger IT systems than standard product and market-focused projects as well.
These are seven important principles of PRINCE2:
- Starting a project
- Directing a project
- Initiating a project
- Controlling a project
- Managing product delivery
- Managing a stage boundary
- Closing a project
Used to define roles and back controls. Not only that but PRINCE2 can be used to deliver a ton of individual project management tasks, such as stage management, product delivery management, and start and end project.
Who Can use PRINCE2: Due to PRINCE2’s diverse nature of project management, it is very suitable for large business projects with a large number of project stakeholders. it will take more time.
7. Six Sigma

Unlike other methods, Six Sigma is used for quality management and is defined as a philosophy rather than a conventional method. It is usually paired with a soft or Agile framework, known as lean Six Sigma and Agile Six Sigma.
The main purpose of Six Sigma is to continuously improve processes and eliminate errors. This is achieved through the continuous development of field experts to maintain, define, and control processes.
To take this approach one step further, you can use the DMAIC process for Six Sigma, which creates a phased approach. These categories include:
Explain: Create project scope, business case, and first standing meeting.
Rate: Collect data that helps inform development needs.
Analyze: Get to the root of the problem.
Upgrade: Solve the causes found.
Management: Work on stabilizing solutions for future projects.
Who can use: Six Sigma is best for large organizations, usually those with a few hundred or more employees. That’s when the need to eliminate project waste begins to have a major impact on your organization.
8. Critical path method (CPM)

What it is: The critical path method involves identifying and planning critical steps within a project by using dependencies, tracking goals and progress, prioritizing deliverables, and managing due dates for all activities that resemble a work breakdown structure.
In this methodology, milestones and deliverables are properly mapped so that successful projects can be done at scale.
Who should use it: CPM is best suited to smaller and mid-sized projects and teams, given that large projects may have multiple stakeholders and multiple deliverables; therefore, the CPM can’t manage complex projects well.
9. Critical chain project management (CCPM)

What it is: While closely related to the critical path methodology, the critical chain project management framework provides more detail, making it among the most comprehensive options.
Critical chain project management methodology:
CCPM is a work breakdown structure like CPM with specific time requirements for each task. This makes task tracking more effective by clearly indicating when tasks are going over their allotted time. The resource leveling technique is also used in order to distribute work across resources when large workloads are present.
Project management tools not only boost efficiency and productivity but also help connect work to project goals. Many include visuals so team members can visualize goals better, creating an organized plan for the team.
Who should use it: CCMP is a wonderful method for working on projects with both small and large teams, as they are primarily used to improve project efficiency. It can also be useful for reporting work in progress to leadership.
10. Lean

What it is: By reducing waste with lean project management, you are creating a simple framework for project requirements. Overall, this means maximizing efficiency and teamwork by doing more with less.
Originally, waste reduction referred to a physical product but has now come to mean wasteful practices. It is represented by three Ms:
Muda (wastefulness): Resource-consuming, but non-value-adding practices
Mura (unevenness): It results from overproduction and leaves behind waste
Muri (overburden): This occurs when resources are overstrained
Project managers are responsible for preventing the three Ms so that projects run smoothly and processes are streamlined. RUP, also aimed at reducing waste, employs a similar approach. In contrast, RUP aims to reduce development costs instead of wasting resources.
Who should use it: Because lean is all about eliminating waste, it’s the most appropriate method for teams struggling to achieve efficiency. This can help team members of all sizes achieve efficiency, although it’s more effective for large organizations.
Conclusion:
How you choose your project methodology will determine the way you communicate with your teams and the type of work you do. However, the way you choose an approach or technique to project methodology will depend on the types of teams, the projects you do, and the types of projects you undertake. Some methodologies facilitate speed, while others focus on efficiency and profitability. Every one of these project management methodologies has pros and cons, so choosing the right one will make your projects flow more smoothly and your teams more effective. Understanding that what worked for one team may not work for you is vital. We recommend testing a few of these and seeing how well they fit into your project.
References:
https://asana.com/resources/project-management-methodologies
https://tms-outsource.com/blog/posts/project-management-framework/
https://kissflow.com/project/project-management-methodologies-and-frameworks/
https://whatis.techtarget.com/definition/project-management-framework
https://monday.com/blog/project-management/project-management-framework/
Author Name: 1. Akshada Padalkar. 2. Rutuja Pawar. 3. Rushikesh Shelke. 4. Sunita Patil.
Guide By: Prof. Vijay Itnal.
